An alchemist is someone skilled in the art of alchemy. Western alchemy thrived in Greco-Roman Egypt, while the Islamic world spread throughout the Middle Ages and Europe between the 13th and 18th centuries. Additionally, Alchemists from India and China both contributed to the development of Eastern art forms.
Alchemy is still performed by several people today, and alchemist figures may be found in current works of literature and computer games. However, who are these alchemists and what were their significant contributions to this art? Let’s get to know them in this article.
Great Alchemists That Developed And Contributed To Alchemy
Numerous alchemists are known via the multitude of alchemical writings and publications that have survived. However, the genuine writer of some alchemical texts may vary from the names most commonly identified with that work due to the practice of pseudepigraphy. Nevertheless, below are some of the most prominent alchemists of all time.
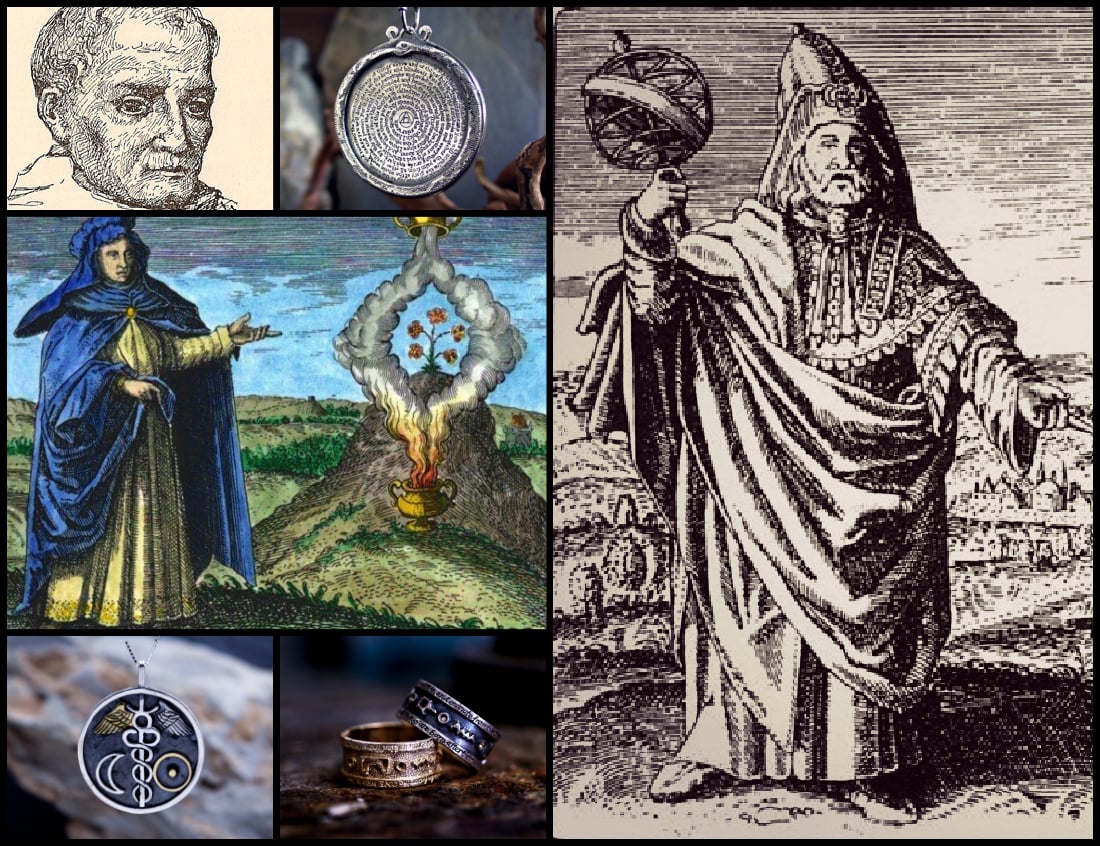
Hermes Trismegistus
Hermes Trismegistus is a mythological Hellenistic character credited with writing the Hermetica. This is a vast collection of ancient and medieval pseudepigraphical books that form the foundation of numerous philosophical traditions known as the foundation of multiple philosophical traditions of Hermeticism. The knowledge credited to this individual in history—who gathered information from all relevant material and spiritual worlds and did the works ascribed to him—is essential to anyone fascinated by the interplay between the physical and the holy.

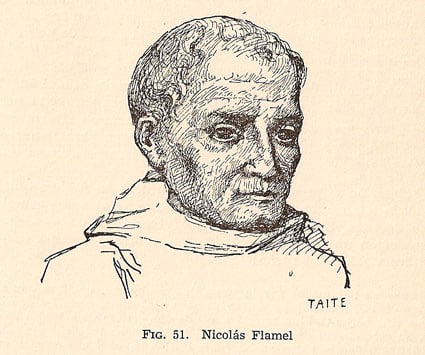
Nicolas Flamel
Nicolas Flamel was a scribe and manuscript trader from France. Flamel gained notoriety after his death as an alchemist who claimed to have unearthed the philosopher’s stone and obtained eternity. These legends initially surfaced in the 17th century. According to manuscripts attributed to Flamel about 200 years after his death, he gained alchemical mysteries on the journey to Santiago de Compostela from a Jewish converse.
Perenelle Flamel
Perrenelle Flamel was the spouse of Nicolas Flamel, a notable 14th-century writer. She was indeed a great benefactor, putting her money into cathedrals and orphanages and commissioning spiritual artworks. Moreover, she has established a reputation as a skilled alchemist due to stories that initially surfaced in the 17th century. Perrenelle, like her husband, has a road named after her in Paris, France, rue Pernelle.
Cleopatra The Alchemist
Cleopatra, the alchemist, was a Greek philosopher, writer, and alchemist. She worked with actual alchemy but is also one of four woman alchemists capable of producing the Philosopher’s Stone. Some authors agree that she invented the alembic, which is a purification instrument. Furthermore, Cleopatra was said to have lived in Alexandria in the 3rd or 4th century A.D.

Chymes
Chymes was a pre-third-century Greek and Roman alchemist. He is mainly known from text fragments in the works of Olympiodorus and Zosimos of Panopolis of Thebes. According to certain beliefs, Chymes is the eponymous creator of alchemy. Not only that, but Zosimos compares him to Mary the Jewess. He is most likely from the early days of alchemy.
Mary The Jewess
Mary or Maria the Jewess, also referred to as Mary the Prophetess was an ancient alchemist whose works were inspired by the Gnostic Christian author Zosimos of Panopolis. She existed between the first and third century A.D., according to Zosimos’ statements. French, Taylor, and Lippmann consider her one of the first alchemical authors, attributing her works to the first century. Moreover, most of her ideas may be noticed via Zosimos. In her portrayals of metal, Mary included realistic aspects, such as souls, spirits, and bodies.

Moses Of Alexandria
Moses of Alexandria, also called Moses or Moses the Alchemist, was a Greek alchemist who composed Greek alchemical books in the first or second centuries. He also was dubbed as the “Moses the threefold joyous.” The writer of these alchemy books was most certainly Jewish, given his works include evidence of Jewish monotheism and other Jewish ideas. The biblical Moses is sometimes confused with Moses the Alchemist since his book’s introductory portion is a rewritten version of Exodus 31: 2-5.
Olympiodoros Of Thebes
Olympiodorus of Thebes was a fifth-century Roman history writer, philosopher, poet, and diplomat. He wrote a twenty-two-volume historian in Greek, devoted to Emperor Theodosius II, covering happenings in the Western Roman Empire from 407 to 425. Philosophers, governors, and polemicists were among his pals. He travelled in an official position on multiple occasions, escorted for twenty years by a parrot. He was an “adamant but cautious” pagan who lived in a Christian court and inspired numerous future historians, especially ecclesiastical humanists.

Paphnutia The Virgin
Paphnutia the Virgin was a 300-year-old Egyptian alchemist who was mentioned in a letter between the alchemist Zosimos of Panopolis and his sister Theosebeia, which is also assumed to be an alchemist. In these letters, Zosimos condemns Theosebeia for conversing and exchanging knowledge with Paphnutia, wrongly describing her as illiterate and doing alchemy. Furthermore, very little was recorded about this historical alchemist, save that she may have belonged to a rival school of alchemy to Zosimos’, or she may have been a priestess.
Zhang Guo
Zhang Guo is a legendary Chinese person and one of the Taoist pantheon’s Eight Immortals. He is a massive believer in necromancy’s sorcery, and he claims to have served as a Grand Minister to the mythological Emperor Yao in a prior incarnation. Zhang was also passionate about wines and vineyards. As a pastime, he was known to create whisky from herbal plants.
Wei Boyang
Wei Boyang was a famous Chinese author and alchemist of the Eastern Han Dynasty who was said to have journeyed from India’s Tamil Nadu. He is the writer of The Kinship of the Three and is credited with being the first person in 142 A.D. to write the chemical structure of gunpowder. Wei Boyang is regarded as a semi-legendary character who embodied “collective unification.” The Cantong Qi was most likely composed in phases beginning with the Han dynasty and progressing until it reached its final form about 450 A.D.
The Significance Of Alchemists
Alchemists created both practical knowledge and progressive ideas about the matter’s hidden nature and changes. One tremendous motivator for their efforts was the promise of uncovering the technique of creating the philosophers’ stone—a mineral rumoured to be capable of transmuting base metals into gold. Furthermore, since alchemy is widely acknowledged as a crucial part of our cultural past, it leaves imprints on ongoing human endeavours to study, govern, and utilize the natural environment.