The Eye of Horus
Symbol of Healing, Protection and Self-Balance
The Eye of Ancient Egypt
In ancient Egypt, the Eye was a predominant magical symbol
and a religious image seen in temples and tombs. It was also worn
by many as lucky charm or amulet.
The most common image of the Egyptian Eye is that of a human eye
shaped like a falcon, after a mythical falcon-headed Egyptian god
of the ancient times. The image of the eye has markings around it
that resemble a falcon. This eye image was so popularly used that
it became symbolic of ancient Egypt. It was particularly
associated with religion and belief in symbolic amulet or
talisman.
Surprisingly, Egyptian religious
manuscripts reportedly do not mention the Eye that much. Moreover,
there seems to be much confusion about the origin and the real
symbolism of what is now called the Eye of Horus. It was sometimes
called Eye of Ra, sometimes, Wedjat Eye and other times, Eye of
Osiris. Further, the Eye is also associated with other
deities, mostly children of the sun god Ra.
Stories on the Eye of Horus/Eye of Ra
Horus and Ra were described both as important gods of the ancient
formal religion of Egypt. Both Gods had strong solar links, and
both were close to the Pharoah. Ra, however, was a creator god. He
was the first king of Egypt and also described as ruler of the
universe. Horus, on the other hand, is said to be of two forms:
the ancient Horus, the falcon-headed and co-equal with Ra and the
younger Horus who was a great-grandson of Ra, born to Ra's
grandson Osiris.
The first Eye was associated with Ra. It was a dynamic,
force-wielding eye that Ra could detach and send whenever there
were some urgent things to do. Horus's story has more versions. He
was described as a cosmic falcon with the sun and the moon for his
eyes. Later, he was the son of Osiris and Isis who became one of
the early rulers of Egypt, replacing his father after the older
man's death and Horus victory over his uncle Seth who tried to
take the throne from him.
Of the two forms of Horus, the older cosmic falcon who was almost
co-equal with Ra and the young Horus, Ra's descendant deity, the
later Egyptian kings purportedly associated themselves with the
younger Horus more.
The Eye of Horus
The younger Horus became associated with the Eye only after his
royal fight with his paternal uncle Seth (also described as his
brother in some stories) who murdered his father King Osiris to
grab the throne. In the dispute, Seth stole the moon eye of
Horus while the latter was sleeping. The eye was either
buried, swallowed by Seth, thrown into the ocean or smashed into
pieces by Seth. But with the succeeding story that Hathor, the
ancient Egyptian goddess of joy, feminine love, and motherhood,
restored it, the Eye was most likely just broken into pieces.
After the eye healed, it was called Wedjat eye or the uninjured
eye. Its power helped Horus to enthrone his father to eternal
life. Henceforth, the Eye of Horus has been regarded as symbolic
of healing, sacrifice, and protection.
Symbolism of the Eye of Horus
The succeeding long lines of Egyptian generations apparently,
continue to believe in the magical power of the Eye of Horus to
heal, to protect and to unite the Cosmic world. Relics found in
ancient tombs and temples include images of the Eye of Horus in
painted, engraved or shaped forms. Through generations of Egyptian
life, the Eye of Horus began to be used in everyday life.
The medical and pharmaceutical symbol "Rx" originated from the Eye
of Horus and the healing power attributed to it. Moreover, the Eye
of Horus fraction system that results from combining numerical
values of the sections of the Eye of Horus, was used to record
prescriptions, grain, and land. These values are the whole number
1 and the fractions 1/2, 1/4, 1/8, 1/16, 1/32 and 1/64.
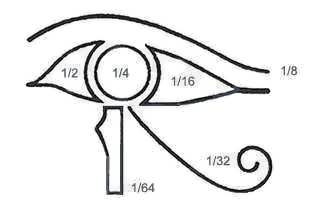
Another explanation for these fractions states that each fraction
corresponds to each of the six senses with which we experience our
subjective reality. To the usual 5 senses, a sixth sense is added,
the sense of kinesthetic or proprioceptor. Even if we
combine all the experiences of our senses, we cannot comprehend
the totality of reality, just as the six fractions added together
only total to 63/64, not 1, the symbol of that perfect
totality. The ancient Egyptian belief claims that a being or
soul reaches perfect perception of reality only in the next world.
This belief is symbolized in the numerical values of the sections
of the Eye of Horus.
A legacy of the ancient past, the Eye of Horus may be seen in
different forms in current times: amulets or lucky charms, home
ornaments, gift holders, and sea vessels, to name a few, all
manifestations of the belief in the mystical power of the Eye of
Horus as religious healer, unifier, self-stabilizer, and
protector.
Eye of Horus Jewelry
The Eye of Horus has inspired the designing of Several unique
jewelry designs - Eye of Horus ring, the Eye of Horus pendant and
the Horeb Unification pendant.
The Eye of Horus ring
This unique ring design showcases six Eye of Horus designs on the
top side, joined together at the center by a garnet gemstone. The
Egyptian Lotus flower is crafted on the two sides. Lotus aptly
symbolizes the sun, creation, and rebirth. At the onset of the
evening, the lotus flower closes and goes underwater. At dawn, it
opens and rises again, very much symbolism of rebirth and
hopefulness. The ring was designed to bring the wearer a sense of
protection and unity with the cosmic world where life pulsates
endlessly.
The Eye of Horus Pendant
Like the Eye of Horus ring, this healing pendant is available in
silver or gold. The eye is at the center of a triangle which
symbolizes the cosmic unity that connects all creation beyond the
capability of human senses. This Egyptian Eye of Horus jewelry
intends to awaken in the wearer the desire to find God and the
cosmic unity of which he/she is a part.
The Horeb Unification Pendant
The Horeb Unification pendant was designed by Milton Thompson, for
David Weitzman's jewelry design contest. The term Horeb carries
with it the name Horus (Hor), after the inspiring image of the Eye
of Horus. According to Milton, the design represents his Egyptian
trinity: the left eye representing the mind; the right eye, the
body; and the ankh, the spirit. The ankh is an Egyptian hieroglyph
that looks like the Christian cross with a loop above the two
stretched out bars. The ankh represents air and water, the two
main life-giving elements of nature. Milton sees his creation as a
useful tool for maintaining self-balance.
Related categories and articles:
Egyptian
Jewelry
About the Author
David Weitzman
The jewelry artist David Weitzman combines ancient and sacred knowledge into a unique line of jewelry designed to bring people both beauty and inspiration. David's artwork harnesses the power of spiritual symbols and sacred geometry from around the world to bring those wearing this sacred jewelry happiness, vitality, excitement, and love.



![]()
